Biliary Atresia Symptoms in Children. Abstract Biliary atresia is the absence of bile excretion which is important for fat absorption.
Biliary Tract Anomalies Obgyn Key
It is the most common indication for liver transplantation in childhood.
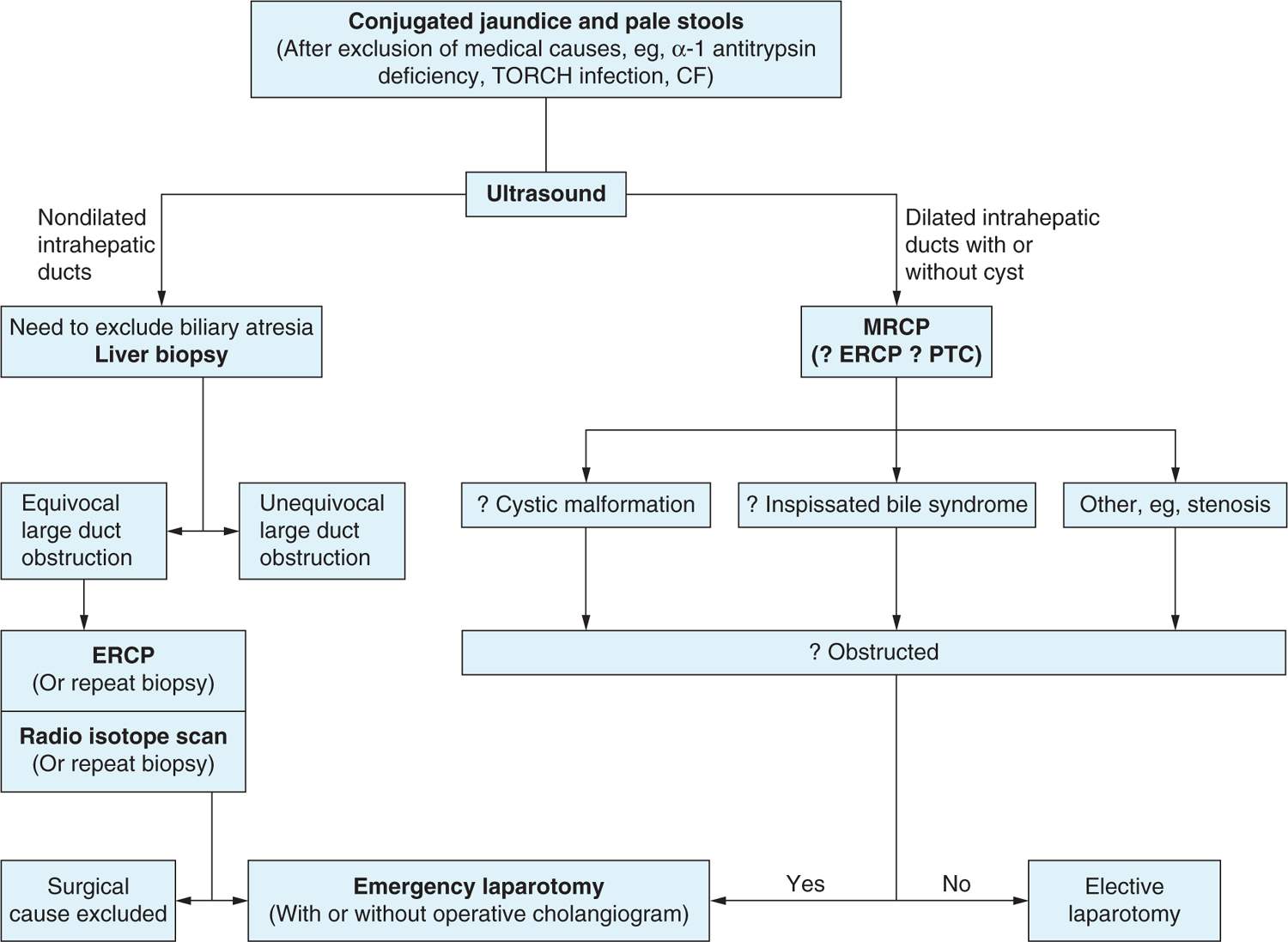
Definitive diagnosis of biliary atresia. On the basis of intraoperative cholangiography results infants were divided into those with a definitive diagnosis of BA and those misdiagnosed with BA. To diagnose biliary atresia a doctor will ask about your infants medical and family history perform a physical exam and order a series of tests. In infancy overlapping clinical patterns of cholestasi.
Electronics Bazaar is one of best Online Shopping Store in India. The value of preoperative liver biopsy in the diagnosis of extrahepatic biliary atresia. Biliary atresia is obstruction of the biliary tree due to progressive sclerosis of the extrahepatic bile duct.
Diagnosis is by blood tests ultrasonography liver biopsy and hepatobiliary scan. The gold standard for the definitive diagnosis of the extrahepatic biliary atresia is. A serious disease requiring prompt early diagnosis preferably before age 6-8 weeks.
Additionally clinical laboratory and imaging features of this condition overlap with those of other causes of cholestasis. Out of 147 infants there was a misdiagnosis of BA in 10 68 infants. Since the definitive diagnosis of biliary atresia BA currently depends on surgical cholangiography identification of noninvasive biomarkers for BA is urgently needed to simplify the diagnostic.
The most definitive finding for non-invasive diagnosis of extrahepatic biliary atresia. Biliary atresia BA is the most severe form of obstructive cholangiopathy occurring in infants. Hepatobiliary scintigraphy 3Alkaline phosphate level 4.
Biliary atresia is a rare disease of infancy which has changed within 30 years from being fatal to being a disorder for which effective palliative surgery or curative liver transplantation or both are available. Once biliary atresia is suspected surgical intervention is the only mechanism available for a definitive diagnosis intraoperative cholangiogram and therapy Kasai portoenterostomy. Early diagnosis of extrahepatic biliary atresia EHBA is very important for a successful bile drainage procedure.
The diagnosis may be made. Crossref Medline Google Scholar 4 Tan Kendrick AP Phua KB Ooi BC Tan. Diagnosis is by blood tests ultrasonography liver biopsy and hepatobiliary scan.
See also Overview of Congenital Gastrointestinal Anomalies The incidence of biliary atresia in the US is about 18000 to 1. Good outcomes for infants depend on early referral and timely Kasai portoenterostomy and thus a high index of suspicion is needed for investigation of infants with persistent. An urgent and extensive investigation is warranted to make a differential diagnosis of EHBA from other cholestatic disease especially neonatal hepatitis NH.
The purpose of this study was to determine if percutaneous cholecysto-cholangiography PCC prevents unnecessary laparotomy in. See also Overview of Congenital Gastrointestinal Anomalies Overview of Congenital Gastrointestinal Anomalies Most congenital gastrointestinal GI anomalies result in some type of intestinal. Definitive diagnosis of BA usually relies on operative findings together with supporting pathological patterns found in the extrahepatic bile duct.
Presentation may include jaundice pale stools or hepatomegaly. Our aim was to evaluate the efficacy of ultrasonographic US examination in the pre-operative diagnosis of biliary atresia BA with special reference to the presence or absence of extrahepatic bile duct. Jaundice a yellow appearance of the skin and whites of the eyes that does not improve within one to two weeks.
The differential diagnosis of neonatal cholestasis is lengthy with extrahepatic biliary atresia being the most common single cause 33. Biliary atresia is a cause of prolonged jaundice which is jaundice occurring for 14 days. Following a thorough evaluation for causes of neonatal cholestasis intraoperative cholangiography establishes the diagnosis of extrahepatic biliary atresia.
For this reason a fat-soluble vitamin deficiency is often found at the time of diagnosis. Experts recommend testing for biliary atresia and other health problems in infants who still have jaundice 3 weeks after birth. Biliary atresia is obstruction of the biliary tree due to progressive sclerosis of the extrahepatic bile duct.
This document is only valid for the day on which it is accessed. A systematic review and meta-analysis J Pediatr. Liu B Cai J Xu Y Peng X Zheng H.
Biliary Atresia BA is the commonest neonatal liver disease in New Zealand affecting 1 in 8000 live births with increased frequency in Maori and Pacific children approximately 1 in 5000. It is a highly reliable test that offers a means of arriving at an early definitive diagnosis of EHBA. A fibro-obliterative obstruction of the extrahepatic biliary tree progressing to intrahepatic ducts which can develop in utero or during the neonatal period.
Biliary atresia should be excluded in. Symptoms of biliary atresia usually begin to appear between two and six weeks after birth and include. Diagnosing biliary atresia is challenging because no single method provides a definitive diagnosis.
Idiopathic neonatal hepatitis a diagnosis made commonly in the past is now an. This approach suffers from the disadvantage that sick infants are subjected to a time-consuming and potentially negative surgical exploration. Thirty consecutive neonates and infants aged 8 to 169 days mean.
Diagnosis investigations A definitive diagnosis of biliary atresia is made by an intraoperative cholangiogram showing biliary obstruction. Options is. Definitive exclusion of biliary atresia in the infant with cholestatic jaundice usually requires operative cholangiography.
62 days suspected of having. Dark yellow or brown urine due to excessive bilirubin in the bloodstream that passes to. Eur J Pediatr Surg 199881216.
Ultrasonographic triangular cord.

Pdf Optimizing The Us Diagnosis Of Biliary Atresia With A Modified Triangular Cord Thickness And Gallbladder Classification

Ultrasound Evaluation Of Biliary Atresia Based On Gallbladder Classification Is 4 Hours Of Fasting Necessary Zhou 2019 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library
Tidak ada komentar